Updated: August, 2025
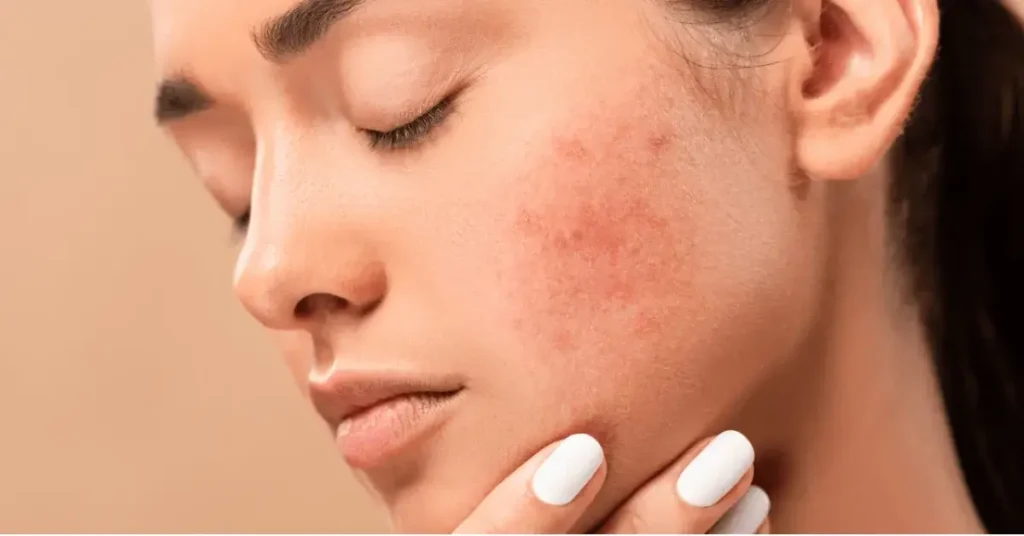
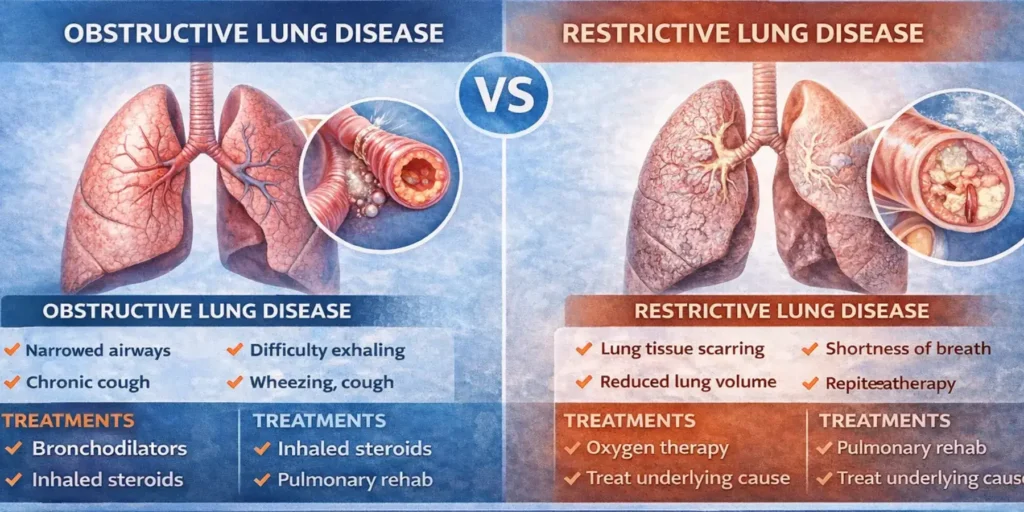
A prevalent skin illness termed pimple is triggered by plugged hair growth follicles behind the surface of the skin. Infections, sometimes referred to as pimples or zits, appear when dead skin cells and sebum—an oil that helps prevent skin from drying out—clog pores. Acne is common for oily skins.
Although the back, chest and shoulders can occasionally have outbreaks, the face is the most frequent region. The skin condition known as acne is inflamed and affects the oil glands, called sebaceous glands, that connect to the hair follicles that house the fine hairs. The pore, a follicular aperture, allows sebum produced by the sebaceous glands to spill onto the skin’s surface in healthy skin. The follicle is lined with keratin cells another sort of skin cell. Typically, when the skin breaks down.
Types of Acne
Pimple forms
Multiple kinds of tumor’s, or acne breakouts, get triggered by acne. Come done in are medical term for swollen or clogged hair follicles. Acne comes in multiple types.
White heads
A white pile caused by stopped hair growth follicles that reside under the skin.
Black heads
Plugged follicles which crack open once they reach the skin’s surface are known as blackheads. Rather than being dirty, the reason they seem black on the skin’s surface is because the sebum is tainted by the air.
The pores
Inflamed lesions that typically resemble little, pink pimples on the skin and may feel sensitive. Pustules, sometimes called pimples, are papules topped with sores filled with white or yellow pus that may have a red base.
Nodules
Enormous, terrible solid lesions lying deep under the skin.
Acne Treatment
Medical professionals and investigators have determined that acne can be caused by one or more of the following:
- significant or accelerated oil generation inside a pore.
- a buildup of dead skin cells within the aperture.
- Bacterial development within the pore.
- Wash the skin in the afflicted regions no more than twice a day.
- Wash the skin in the troubled regions no more than twice a day.
- Use lukewarm water and a little soap or cleanser to wash the troubled region. Overly hot or cold water can make acne worse.
Never try to “clean out” blackheads or pinch spots. The following factors could make you more likely to develop acne:
Acne Impact on Hormones
Acne may result from an increase in android, or male sex hormones. During puberty, they usually increase in both boys and girls and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. Acne can also result from pregnancy-related changes in hormones.
- History in the family: According to researchers, having face-prone parents may increase your risk getting acne.
- Drugs: Certain medications including those including hormones.
- Diet: Owing to some research, eating some food could aggravate acne.
- Researchers are still looking at how nutrition may contribute to acne.
- Pressure from backpacks, restrictive clothes and athletics helmets.
- Climatic irritants include high levels of moisture and pollution.
- Rubbing or squeezing imperfections.
- Rubbing too hard on your skin.
Kinds of Acne locations
Acne can cause six primary types of spots:
- They are not filled with dirt;
- Whiteheads resemble blackheads but may be firmer and not release when squeezed;
- Nodules are large hard lumps that develop beneath the skin’s surface and can be painful;
- They are large pus-filled lumps that resemble boils and carry.
- Wash the skin in the afflicted regions no more that twice a day.
- Use lukewarm water and a light soap or cleanser to wash the afflicted area.
- Never attempt to “clean out” pinch spots or blackheads. This may exacerbate them and result in long-lasting damage.
What are causes of acne?
Although it can begin at any age, acne is most frequently associated with the hormonal changes that occur throughout puberty.
The oil-producing glands close to the skin’s hair follicles create more oil (abnormal sebum) when certain hormones are released.
The normal innocuous skin bacterium Pace become more active due to the aberrant sebum production, leading to irritation and pus production.
Additionally, the hormones thicken the follicle’s inner lining, which clogs the pores. Removing this obstruction is not aided by cleansing the skin.
Additional potential reasons
Acne has been connected to family times past. If both of your parents had acne, you are more possible to have it as well. Women may also get acne as a result of hormonal changes, such as those skilled during period or pregnancy. There is no signal that having sex or living ineffectively encourages acne.
Who is impacted with Acne?
Teens and younger adults are prone to acne. Most people experience intermittent acne for several years before their symptoms improve as they age. Acne can occasionally persist until adulthood. In persons over 35, acne affects about 3% of the population.
Use lukewarm water and a light soap or cleanser to wash the afflicted area. Never attempt to “clean out ‘’ pinch spots or blackheads. This may exacerbate them and result in long -lasting damage. Steer clear of oil based makeup, skincare, and sun protection products (often referred to as “comedogenic”).
Use non -comedogenic water-based products; they are less likely to clog your skin’s pores. Use a water¬-based emollient without any smell if dry skin is an issue.
Even today, acne is a highly prevalent inflammatory dermatosis that frequently has a substantial psychological morbidity component. Young adults are usually affected at a period of maximal physical, emotional, and social transformation.
Conclusion
Although acne is not deadly, its intensity can have major psychological repercussions (such as sadness) and leave a victim with scars and discomfort . The sebaceous glands responsible for acne are located on the forehead and face because they provide a selective advantage by ‘lubricating’ the broadest areas of the newborn, facilitating the delivery process.